PDA
What is a patent ductus arteriosus?
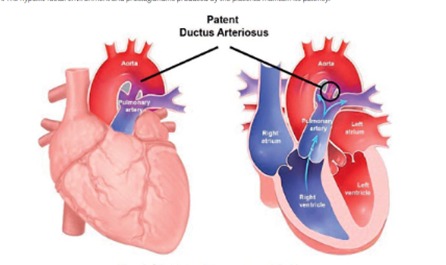
Babies are born with a natural opening in the heart between the aorta and pulmonary artery called the ductus arteriosus. Under normal circumstances, this vessel closes naturally or becomes tiny within the first few days of life. However, in some babies, particularly those born early (premature neonates), this hole remains open. This is called a patent ductus arteriosus or persistent ductus arteriosus.
A patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect where the ductus arteriosus stays open and causes oxygen-rich blood to return to the lungs instead of going to the rest of the body. This means that blood vessels in the lungs have to handle more blood than normal, which causes the heart and lungs to overwork and makes breathing more difficult. A PDA can also cause problems with feeding, weight gain and blood circulation.
Approximately 1 in 2,000 babies (less than 1%) are born with a PDA. Premature babies are significantly more likely to have a PDA (between 20% and 60%). A PDA may be present with other congenital heart defects.
How we treat PDAs
PDA treatment options for premature infants include:
- Observation:Doctors will closely monitor the heart and blood vessel to determine whether the PDA is closing properly or too small to cause a problem.
- Medication:In premature infants, an intravenous (IV) medication called indomethacin may help close a PDA.
- Open-heart surgery:Doctors can also close a PDA through open-heart surgery, where they open the chest between the ribs to tie off or clamp the duct. Babies who have heart surgery face more risk and longer recovery time.
- Transcatheter closure:Doctors can insert a soft, wire mesh PDA closure device through a catheter (a long, narrow tube) to stop blood flow through a PDA.
What is transcatheter PDA closure?
- A transcatheter PDA closure is a minimally-invasive (non-surgical) procedure to close the ductus arteriosus. Specialized heart doctors called pediatric cardiac interventionists use a procedure called cardiac catheterizationto place a small device in the vessel, which closes the PDA.
- This procedure is also called “minimally-invasive PDA closure” or “PDA occlusion.” (Occlusion means blocking or closing a blood vessel.)