 Posted on July 3, 2024
Posted on July 3, 2024
Treatments and Devices for Structural Heart Disease: An Overview by Dr. Girish B Navasundi
Dr. Girish B Navasundi 21 years experience | MBBS, MD (Gen Medicine), DNB (Cardiology) Senior Consultant Interventional Cardiologist & Certified TAVR Specialist, Lead Consultant – Structural Heart Disease & Heart Failure Apollo Hospitals, Bannerghatta Road, Bengaluru, Karnataka
Structural heart disease encompasses a range of conditions affecting the valves, walls, and chambers of the heart. Advanced interventions and innovative devices have significantly improved the management and outcomes of these conditions. Let’s delve into some critical components and devices used in the treatment of structural heart disease.
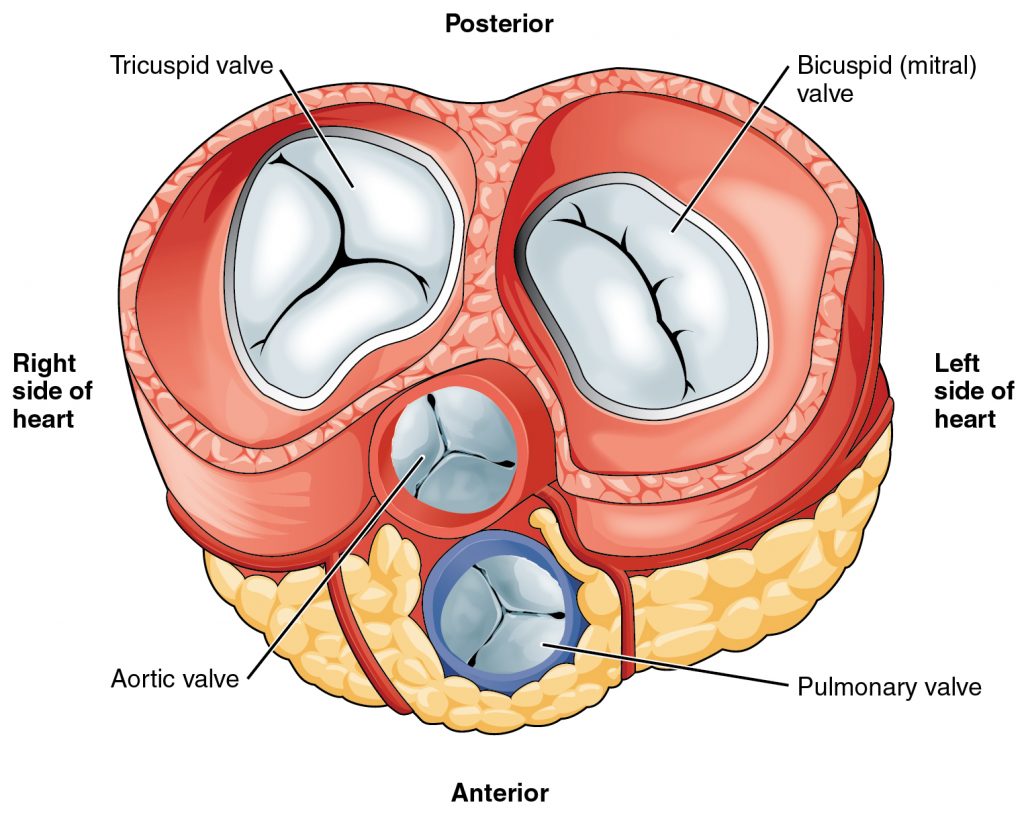
Pulmonary Valve Interventions
The pulmonary valve regulates blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary arteries. Disorders such as pulmonary stenosis and regurgitation can compromise heart function.
- Transcatheter Pulmonary Valve Replacement (TPVR): This minimally invasive procedure replaces the dysfunctional pulmonary valve without open-heart surgery. TPVR is particularly beneficial for patients with congenital heart defects or those at high risk for conventional surgery.
Tricuspid Valve Interventions
The tricuspid valve controls blood flow between the right atrium and right ventricle. Tricuspid regurgitation and stenosis are common issues that can lead to heart failure if untreated.
- Transcatheter Tricuspid Valve Repair (TTVR): TTVR involves using a catheter-based approach to repair the tricuspid valve, reducing regurgitation and improving heart function. This method is suitable for patients who are not candidates for open-heart surgery.
Closure Devices
Closure devices are crucial in managing congenital heart defects such as Atrial Septal Defects (ASD), Ventricular Septal Defects (VSD), and Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA).
- ASD Closure: Atrial septal defect closure involves using a device to seal the hole in the atrial septum, preventing abnormal blood flow between the atria and reducing the risk of heart failure and stroke.
- VSD Closure: Ventricular septal defect closure is similar to ASD closure, targeting the hole in the ventricular septum to normalize blood flow and prevent complications like pulmonary hypertension and heart failure.
- PDA Closure: Patent ductus arteriosus closure involves the insertion of a closure device to seal the abnormal opening between the aorta and pulmonary artery, which helps prevent pulmonary overcirculation and heart failure.
Left Ventricular Assist Device (LVAD)
LVADs are mechanical pumps that support heart function and blood flow in individuals with severe heart failure.
- LVAD: This device is implanted in the chest and assists the left ventricle in pumping blood to the rest of the body. LVADs are often used as a bridge to heart transplantation or as a long-term solution for patients ineligible for transplant.
Cerebral Protection Device
During certain heart procedures, there is a risk of debris entering the bloodstream and causing a stroke. Cerebral protection devices help mitigate this risk.
- Cerebral Protection Device: This device captures and removes debris from the bloodstream during procedures like transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), significantly reducing the risk of stroke.
MitraClip
The MitraClip is a revolutionary device for treating mitral regurgitation, where the mitral valve does not close properly.
- MitraClip: This minimally invasive device clips together a portion of the mitral valve, reducing regurgitation and improving symptoms without the need for open-heart surgery. It is particularly beneficial for high-risk surgical patients.
Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (SAVR)
SAVR is a traditional surgical approach for treating severe aortic valve stenosis.
- SAVR-Robotic: Robotic-assisted SAVR offers precision and reduced recovery time. The robot aids in the surgical procedure, providing enhanced dexterity and control for the surgeon.
- SAVR-MICS (Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery): SAVR-MICS involves smaller incisions compared to conventional SAVR, leading to less pain, faster recovery, and reduced risk of infection. This approach is suitable for patients needing valve replacement but who seek a less invasive option.
Conclusion
Structural heart disease encompasses a wide range of conditions that require specialized interventions and innovative devices for effective management. As a Senior Consultant Interventional Cardiologist with over 21 years of experience, Dr. Girish B Navasundi at Apollo Hospitals is dedicated to providing cutting-edge treatments to improve patient outcomes. From valve interventions to closure devices and advanced surgical techniques, these advancements offer hope and improved quality of life for individuals affected by structural heart disease.
Apollo Hospitals, 154, Apollo Hospitals, 11, Bannerghatta Rd, Opp. I, I.M, Amalodbhavi Nagar, Panduranga Nagar, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560076