 Posted on November 27, 2023
Posted on November 27, 2023
Understanding Structural Heart Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
Structural heart disease, a term that encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the heart’s structure and function. This guide aims to provide comprehensive information about structural heart disease, including its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or just someone interested in learning more about heart health, this post is designed to offer valuable insights.
What is Structural Heart Disease?
Structural heart disease refers to a range of heart conditions that involve defects or abnormalities in the heart’s structure. This can include issues with the heart’s valves, walls, or chambers. Unlike coronary artery disease, which is caused by the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries, structural heart disease is often congenital (present at birth) or develops due to aging, infection, or other factors.
Types of Structural Heart Disease
- Congenital Heart Defects: These are heart abnormalities present at birth. They can range from simple issues like a small hole in the heart to complex abnormalities that severely affect how blood flows through the heart.
- Valvular Heart Disease: This involves damage to or a defect in one of the four heart valves. Examples include aortic stenosis, mitral regurgitation, and mitral valve prolapse.
- Cardiomyopathies: This group of diseases affects the heart muscle itself, potentially leading to heart failure. Examples include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Atrial and Ventricular Septal Defects: These are holes in the walls between the atria or ventricles of the heart, respectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of structural heart disease can vary based on the specific condition. Congenital heart defects are often due to genetic factors or environmental exposures during pregnancy. Other forms of structural heart disease can develop due to:
- Aging
- Infections (like rheumatic fever)
- High blood pressure
- Heart attack
- Connective tissue disorders
Symptoms to Watch For
Symptoms of structural heart disease can vary widely but may include:
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Fatigue
- Swelling in the legs, ankles, or abdomen
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats
- Fainting or dizziness
Diagnosing Structural Heart Disease
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of:
- Physical Examination: Listening to the heart for abnormal sounds.
- Imaging Tests: Such as echocardiograms, MRI, or CT scans.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): To measure the heart’s electrical activity.
- Cardiac Catheterization: A procedure to closely examine the heart.
Treatment Options
Treatment for structural heart disease depends on the specific condition and its severity. Options may include:
- Medications: To manage symptoms or prevent complications.
- Surgical Procedures: Such as valve repair or replacement, or surgery to repair structural defects.
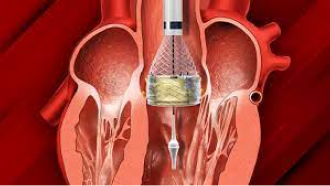
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Like transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR).
Living with Structural Heart Disease
Living with structural heart disease often involves regular medical care and lifestyle adjustments. Patients may need to:
- Follow a heart-healthy diet
- Engage in regular physical activity as advised by a healthcare provider
- Monitor and manage other health conditions
- Attend regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare team
Conclusion
Structural heart disease encompasses a wide range of conditions, each requiring specialized care and management. Advances in medical science have significantly improved the outlook for many people with these conditions. If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with structural heart disease, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare team to understand your specific condition and the best treatment plan.
Remember, early detection and treatment can make a significant difference in managing structural heart disease. Stay informed, stay proactive, and take heart – there’s much that can be done to live a full and healthy life with structural heart disease.